Enter the query into the form above. You can look for specific version of a package by using @ symbol like this: gcc@10.
API method:
GET /api/packages?search=hello&page=1&limit=20
where search is your query, page is a page number and limit is a number of items on a single page. Pagination information (such as a number of pages and etc) is returned
in response headers.
If you'd like to join our channel webring send a patch to ~whereiseveryone/toys@lists.sr.ht adding your channel as an entry in channels.scm.
This package provides Haskell bindings to SDL2_image.
This package provides a configuration management library for programs and daemons. The features include:
Automatic, dynamic reloading in response to modifications to configuration files.
A simple, but flexible, configuration language, supporting several of the most commonly needed types of data, along with interpolation of strings from the configuration or the system environment (e.g.
$(HOME)).Subscription-based notification of changes to configuration properties.
An
importdirective allows the configuration of a complex application to be split across several smaller files, or common configuration data to be shared across several applications.
This Haskell library provides implementations of special mathematical functions and Chebyshev polynomials. These functions are often useful in statistical and numerical computing.
This package provides an abstraction for communicating with line-oriented network services while abstracting over the use of SOCKS5 and TLS (via OpenSSL)
This library implements the 'patience diff' algorithm, as well as the patience algorithm for the longest increasing subsequence problem. Patience diff computes the difference between two lists, for example the lines of two versions of a source file. It provides a good balance between performance, nice output for humans, and simplicity of implementation.
This package provides a type-safe tool for generating XML code via quasi-quoting built on top of ghc-shakespeare.
This library provides a utility function liftType, which accepts a type application argument and returns the Template Haskell Type representation of it.
Bindings to the Xft, X Free Type interface library, and some Xrender parts.
This package provides an abstract class to manipulate sequence of bytes. The use case of this class is abstracting manipulation of types that are just wrapping a bytestring with stronger and more meaniful name.
This package contains the generics system described in the /Scrap Your Boilerplate/ papers (see the website). It defines the Data class of types permitting folding and unfolding of constructor applications, instances of this class for primitive types, and a variety of traversals.
Provides Default instances for types from the old-locale package.
This package provides a means of generating tag files for Emacs and Vim.
__This package is deprecated__. Please, use genByteString from the [random package (version >=1.2)](https://hackage.haskell.org/package/random) instead. . Efficient generation of random bytestrings. The implementation populates uninitialized memory with uniformily distributed random 64 bit words (and 8 bit words for remaining bytes at the end of the bytestring). . Random words are generated using the PRNG from the [mwc-random](https://hackage.haskell.org/package/mwc-random) package or the [pcg-random](https://hackage.haskell.org/package/pcg-random) package. It is also possible to use a custom PRNG by providing an instance for the RandomWords type class and using the function generate from the module "Data.ByteString.Random.Internal". . The generated byte strings are suitable for statistical applications. They are /not/ suitable for cryptographic applications. . 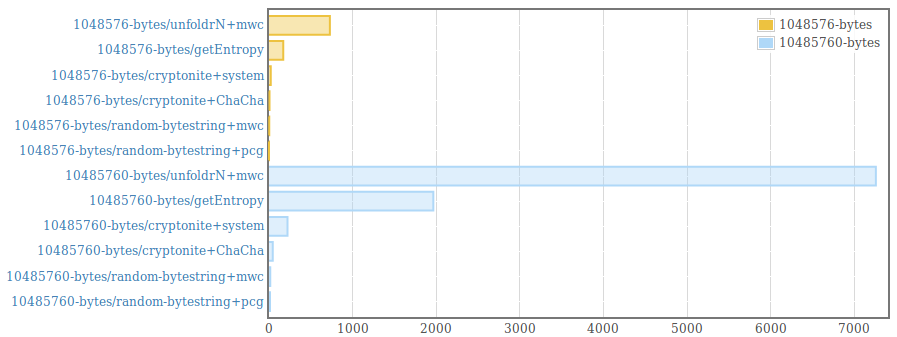 . 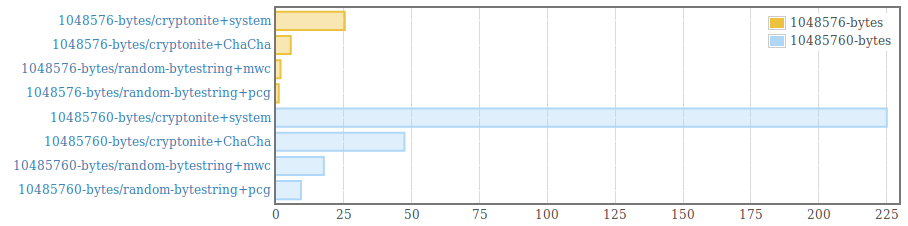
This library provides Haskell bindings for the OpenGL Utility Toolkit, a window system-independent toolkit for writing OpenGL programs.
This library provides tools to calculate various string metrics efficiently.
This package provides a Pure Haskell implementation of the SplitMix pseudorandom number generator. SplitMix is a "splittable" pseudorandom number generator that is quite fast: 9 64-bit arithmetic/logical operations per 64 bits generated. SplitMix is tested with two standard statistical test suites (DieHarder and TestU01, this implementation only using the former) and it appears to be adequate for "everyday" use, such as Monte Carlo algorithms and randomized data structures where speed is important. In particular, it should not be used for cryptographic or security applications, because generated sequences of pseudorandom values are too predictable (the mixing functions are easily inverted, and two successive outputs suffice to reconstruct the internal state).
This library provides mechanisms to efficiently run periodic, on-demand actions in Haskell.
This package provides Prism and Traversals for These.
Monad classes using type families, with instances for various monad transformers, inspired by the paper 'Functional Programming with Overloading and Higher-Order Polymorphism', by Mark P Jones. This package is almost a compatible replacement for the mtl-tf package.
This is a pretty printing library based on Wadler's paper "A Prettier Printer". It has been enhanced with support for ANSI terminal colored output using the ansi-terminal package.
This library provides profunctors for Haskell.
This package provides instances defined in later versions of ghc-binary package.
Pandoc is a Haskell library for converting from one markup format to another, and a command-line tool that uses this library. It can read and write Markdown and (subsets of) other formats, such as HTML, reStructuredText, LaTeX, DocBook, and many more.
Pandoc extends standard Markdown syntax with footnotes, embedded LaTeX, definition lists, tables, and other features. A compatibility mode is provided for those who need a drop-in replacement for Markdown.pl.
This library lets you write interactive programs without callbacks or side-effects. Functional Reactive Programming (FRP) uses composable events and time-varying values to describe interactive systems as pure functions. Just like other pure functional code, functional reactive code is easier to get right on the first try, maintain, and reuse. Reflex is a fully-deterministic, higher-order FRP interface and an engine that efficiently implements that interface.